JAVASCRIPT UI
Javascript-powered UI Components
Create interactive pages, no javascript required!
Ink’s vast array of UI components can be used in combination to create rich, interactive pages. They are many, and are very flexible. Javascript is not required for a lot of cases, but if you want to do more advanced stuff, you have to write some of it.
To get started, include the following JS files in the bottom of your HTML:
<!-- Load the js files -->
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://ink.freetls.fastly.net/3.1.10/js/ink-all.js"></script>
<!-- Autoload is required for the examples on this page. Read more below. -->
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://ink.freetls.fastly.net/3.1.10/js/autoload.js"></script>Autoload
Although this is a page for Javascript-powered components, You will only find pure HTML examples on this page. That is because, thanks to Autoload (the autoload.js file you loaded above) you don’t need to write any Javascript to do most things.
autoload.js is a small Javascript file that avoids a lot of boilerplate javascript to create the UI components on this page. It does so by initializing these elements automatically (new Component(componentElement, options)) based on their CSS class, so you don’t have to.
All Ink UI components are registered to be loaded in Autoload, with a class similar to their name. For example, to create a Modal, you add the .ink-modal class to an element. To create a Toggle, you add a .ink-toggle class to an element, and so on.
If you want, you can disable this behaviour. Just add data-autoload="false" to elements without autoload, or don’t include autoload.js at all to disable it completely.
A note on option names (data-option-name vs optionName)
All configuration options, except callback functions, are available as data-attributes but are prefixed with data- and are written in lowercase and hyphen separated: someOption (as passed in javascript) is the same as data-some-option (as passed in HTML).
Using these components with Javascript instead of autoload
In this page, you see a lot of javascript-powered components created only with HTML, but sometimes you need the extra edge – The power to create and destroy components any time you like, or to pass callbacks and arbitrary objects.
// This is a simple example for Toggle.
// For other components, you can replace "Toggle" below with the component name.
Ink.requireModules(['Ink.UI.Toggle_1'], function (Toggle) {
// Every component is a plain old Javascript class. Its constructor takes two arguments:
// an element on the page and a set of options.
new Toggle('#my-toggle', {
target: '#toggled-element' // This is the same as data-target="#toggled-element"
});
});Carousel
A responsive carousel with one or more slides per page. Cycle back and forth between slides with any content you can put in. You can also swipe back and forth with your finger if your device supports touch.
Most of the time, you will use this in conjunction with Pagination, because you want some sort of way to change pages!
Carousel Examples
Basic example:
This example shows you how to create a basic Carousel, use it together with a basic Pagination. It’s touch-enabled (touch support is on by default) and responsive (because it uses Ink’s CSS grid classes). As you switch to smaller devices, you’ll see that you get less slides per page to better use the viewport space.
Demo
Code
<div id="my-carousel-1" class="ink-carousel" data-pagination="#my-carousel-1-pagination">
<ul class="stage column-group half-gutters">
<li class="slide xlarge-33 all-50 small-100 tiny-100">
<img class="quarter-bottom-space" src="https://lorempixel.com/400/200/sports/1">
<div class="description">
<h4>Title</h4>
<p>Description paragraph</p>
</div>
</li>
<li class="slide xlarge-33 all-50 small-100 tiny-100">
<img class="quarter-bottom-space" src="https://lorempixel.com/400/200/sports/2">
<div class="description">
<h4>Title</h4>
<p>Description paragraph</p>
</div>
</li>
<li class="slide xlarge-33 all-50 small-100 tiny-100">
<h4 class="vertical-space">Hello world!</h4>
<p>Here is a form inside a Carousel:</p>
<form class="ink-form">
<input type="text" placeholder="just because!" />
<button class="ink-button">Go!</button>
</form>
</li>
<li class="slide xlarge-33 all-50 small-100 tiny-100">
<img class="quarter-bottom-space" src="https://lorempixel.com/400/200/sports/3">
<div class="description">
<h4>Title</h4>
<p>Description paragraph</p>
</div>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<nav id="my-carousel-1-pagination" class="ink-navigation">
<ul class="pagination black">
</ul>
</nav>Carousel with chevrons example
This is how you create a Carousel with chevron pagination.
To use a chevron Pagination with it, embed the .ink-pagination element inside the .ink-carousel element and add the chevron class to its ul.
Demo
Code
<div id="my-carousel-2" class="ink-carousel" data-pagination="#my-carousel-2-pagination">
<ul class="stage column-group half-gutters">
<li class="slide all-50 small-100 tiny-100">
<img class="quarter-bottom-space" src="https://lorempixel.com/400/200/sports/1">
<div class="description">
<h4>This is slide 1</h4>
</div>
</li>
<li class="slide all-50 small-100 tiny-100">
<img class="quarter-bottom-space" src="https://lorempixel.com/400/200/sports/2">
<div class="description">
<h4>This is slide 2</h4>
</div>
</li>
<li class="slide all-50 small-100 tiny-100">
<img class="quarter-bottom-space" src="https://lorempixel.com/400/200/sports/3">
<div class="description">
<h4>This is slide 3</h4>
</div>
</li>
</ul>
<nav id="my-carousel-2-pagination" class="ink-navigation">
<ul class="pagination chevron">
</ul>
</nav>
</div>Carousel options
Add the following attributes to your .ink-carousel element to configure your Carousel.
data-pagination="<selector>": Pagination element to use with this Carousel. Don’t forget this!data-initial-page="<page>": Carousel starts inpage. First page is 0.data-space-after-last-slide="false": Don’t leave blank space after the last slide.data-swipe="false": Disable touch support.data-auto-advance="<time>": Auto-advance pages everytimemilliseconds.
You can read the list of options to create the Carousel with JS here.
Advanced Carousel stuff:
You can visit the Carousel API docs to find out about Javascript-only options, javascript methods, and how to create Carousels using Javascript
Close
Dismiss things.
Add the ink-close or ink-dismiss to elements. Those elements, when clicked, will be removed. Plays well with the Alert UI Element.
Close Example
Here’s an example. Click the × sign to close the alert. When you do, the element will be removed from the page.
Demo
Click the X to close this!
Code
<div class="ink-alert basic" role="alert">
<button class="ink-dismiss">×</button>
<p>Click the X to close this!</p>
</div>Close options
(Close has no options)
Advanced Close stuff:
There’s not much to know about Close, but here are the Close JS API docs.
DatePicker
DatePicker is a component for picking dates. You use it together with an input box, and it gets filled with the date in a certain format. The user may change the date by navigating the calendar or by typing in the input box using the correct format.
The date’s format is given in the data-format option, where you pass a date format string in the syntax of PHP’s date() function.
DatePicker Examples
Basic example
This is a simple DatePicker, mostly using the default options. It writes the dates in DD-MM-YYYY format.
Demo
Code
<div class="ink-form">
<div class="control-group column-group no-margin">
<div class="control all-30">
<input type="text" class="ink-datepicker" data-format="d-m-Y" />
</div>
</div>
</div>Ranged example
A DatePicker which only accepts dates between the birth of Aníbal Cavaco Silva and today.
Demo
Pick a day in the life of Aníbal Cavaco Silva:
Code
<p>Pick a day in the life of Aníbal Cavaco Silva:</p>
<div class="ink-form">
<div class="control-group column-group no-margin">
<div class="control all-30">
<input
type="text"
class="ink-datepicker"
data-format="d-m-Y"
data-date-range="1939-07-15:NOW" />
</div>
</div>
</div>Always-open example
This is a DatePicker that never closes. To do this, we set it to not be “shy” (that is, don’t close automatically), and we told it to open automatically.
We also need to hide the “close” button so it doesn’t close on us, and add some CSS so that it doesn’t have position: absolute.
Demo
Code
<div class="ink-form">
<div class="control-group column-group no-margin">
<div class="control all-30">
<input
type="text"
class="ink-datepicker"
data-css-class="ink-calendar my-never-closing-datepicker"
data-format="d-m-Y"
data-shy="false"
data-auto-open="true"
data-show-clean="false"
data-show-close="false" />
</div>
</div>
</div>
<style>
.my-never-closing-datepicker {
position: static;
display: inline-block;
overflow: hidden;
}
</style>DatePicker options
Add the following attributes to your .ink-datepicker input element to configure your DatePicker.
Date options
data-start-date="<yyyy>-<mm>-<dd>": Start with a certain date. Defaults to today.data-date-range="<start>:<end>": Only allow dates betweenstartandend. Don’t forget the::).data-format="d-m-Y": Date format string. Uses the same syntax as PHP’sdate()function. Let’s see how they format the date “15th July of 1939”:data-format="d-m-Y"- “15-07-1939”data-format="Y/d/m"- “1939/15/07”data-format="Y-m-d"- “1939-07-15”
Text and formatting options:
data-clean-text="<word>": Text for the “Clear” button.data-close-text="<word>": Text for the “Close” button.data-of-text="<of>": Text to show between month and year. Defaults to ‘ of ‘.data-next-link-text="<text>": Text for the next button. Defaults to ‘»’.data-prev-link-text="<text>": Text for the previous button. Defaults to ‘«’.data-start-week-day="<day>": First day of the week. Sunday is zero. Defaults to 1 (Monday).
Misc options
data-show-clean="false": Hide the “Clear” button.data-show-close="false": Hide the “Close” button.data-auto-open="true": The DatePicker will be initially openeddata-shy="false": Stop the DatePicker from closing itself automatically.data-css-class="ink-calendar <my classes>": Add classes to the DatePicker.data-on-focus="false": Add this if you don’t want the DatePicker to open itself when you click the input.data-picker-field="<selector>": (if not using in an input[type=”text”]) Element which displays the DatePicker when clicked. Defaults to an “open” link.data-position="right": Float the DatePicker to the right.
Options for using <select> elements instead of an <input> element.
Options to use DatePicker with <select> elements. They require data-display-in-select="true".
data-display-in-select="true": Enable this first.data-day-field="<selector>":<select>field with the days.data-month-field="<selector>":<select>field with the months.data-year-field="<selector>":<select>field with the years.
You can read the list of options to create the DatePicker with JS here.
Advanced DatePicker stuff:
You can visit the DatePicker API docs to find out about Javascript-only options, javascript methods, and how to create DatePickers using Javascript
Draggable
Draggable is a component which works with Droppable.
Draggable Examples
Basic example
Drag some draggables around!
Demo
Code
<span class="ink-label ink-draggable blue">Draggable 1</span>
<span class="ink-label ink-draggable green">Draggable 2</span>
<span class="ink-label ink-draggable orange">Draggable 3</span>Constraints
These Draggables can’t move freely, they’re constrained inside certain boundaries.
Demo
Code
<div id="draggable-constraint" class="example" style="min-height: 300px">
<span class="ink-label ink-draggable blue"
data-constraint-elm="#draggable-constraint">
Drag me inside the box
</span>
</div>Draggable options
data-constraint="<vertical, horizontal or both>"- Constrain Draggable movement in an axis. None by default. Can bevertical,horizontal, orboth. By default movement is not constrained.data-constraint-elm="#my-div"- Only drag inside#my-div. Make sure that element has amin-heightto avoid weird behaviour.data-handle=".drag-here"- The element with the.drag-hereclass will be used as a handle for dragging.data-revert="true"- Revert the draggable to its original position when dropped.data-cursor="pointer"- Set the mouse topointerwhile hovering this Draggable, instead ofmove. Valid options here are the values of the CSScursorproperty.data-z-index="100"- Set the z-index to 100 while dragging.data-fps="12"- Move things at most 12 times per second. Use this to limit the CPU resources needed to perfrom a drag action.data-mouse-anchor="<anchor>"- Anchor for the drag. Can be one of:"left","center","right","top","center","bottom".data-drag-class="im-dragging"- Add the.im-draggingclass when this draggable is being dragged.data-skip-children="false"- Dragging children of this element doesn’t count.
Movement constraints
If you set a data-constraint or data-constraint-elm option (see above), these can be used to determine how far from the constraint areas the Draggable can move. Try them out:
data-top="10"- Always stay 10px away from the top.data-right="10"- Always stay 10px away from the right.data-bottom="10"- Always stay 10px away from the bottom.data-left="10"- Always stay 10px away from the left.
Advanced Draggable stuff:
You can visit the Draggable API docs to find out about Javascript-only options, javascript methods, and how to create Draggables using Javascript
Drawer
Drawer is a component showing off-canvas menus which slide in when their toggle is clicked or touched. It’s useful for saving precious screen real estate on devices with small screens.
It slides in from one of the sides, either pushing or going over (this is configurable) the page’s content.
You need to place your entire page’s content inside an element with the class content-drawer, so that it may be pushed aside.
Drawer Examples
Basic example
This is a simple Drawer coming in from the left.
Demo
Code
<body class="ink-drawer">
<div class="left-drawer" style="background:gray">
Left drawer content...
</div>
<div id="main-content" class="content-drawer ink-grid">
<a class="left-drawer-trigger" href="#">Open drawer</a>
<h1>My page</h1>
<p>
Content of my page...
</p>
</div>
</body>Two drawers example
This is an example of two drawers, one coming from the right and one from the left.
Demo
Code
<body class="ink-drawer">
<div class="left-drawer" style="background:gray">
Left drawer content...
</div>
<div class="right-drawer" style="background:blue">
Right drawer content...
</div>
<div id="main-content" class="content-drawer ink-grid">
<a class="left-drawer-trigger" href="#">Open left drawer</a>
<a class="right-drawer-trigger push-right" href="#">Open right drawer</a>
<h1>My page</h1>
<p>
Content of my page...
</p>
</div>
</body>'over' mode
This drawer goes over the page content, instead of pushing it.
Demo
Code
<body class="ink-drawer" data-mode="over">
<div class="left-drawer" style="background:gray">
<p>Left drawer content...</p>
<p>I am over the main page content!</p>
</div>
<div id="main-content" class="content-drawer ink-grid">
<a class="left-drawer-trigger" href="#">Open drawer</a>
<h1>My page</h1>
<p>
Content of my page...
</p>
</div>
</body>Drawer options
data-mode="over"- Make the drawer go over the body instead of pushing it.data-sides="<side>"- Make a drawer that comes in from thisside. Can be ‘left’, ‘right’, or ‘both’.data-content-drawer="#my-content-div"- Your main page container.data-left-drawer=".my-left-drawer"- Left drawer (the element that is placed offcanvas). This should be a sibling of yourdata-content-drawerelement.data-left-trigger=".my-left-trigger"- Left drawer trigger(s). When you click this trigger, theleftDraweris shown.data-right-drawer=".my-right-drawer"- Right drawer (the element that is placed offcanvas). This should be a sibling of yourdata-content-drawerelement.data-right-trigger=".my-right-trigger"- Right drawer trigger(s). When you click this trigger, therightDraweris shown.
Advanced Drawer stuff:
You can visit the Drawer API docs to find out about Javascript-only options, javascript methods, and how to create Drawers using Javascript
Dropdown
Dropdown is designed to add dropdown menus. They are a simplified version of Toggle, which is much more complex, and they work better with nested menus without a lot of the hassle which goes into creating them using Toggle.
It also includes some mouse-away logic, so as to avoid the dropdown being open forever if your mouse moves away from the dropdown. This is activated using data-dismiss-after="<s>" where s is your time in seconds which it is supposed to stay open.
Dropdown Examples
Basic example
This is a simple Dropdown menu.
Demo
Code
<div class="ink-dropdown" data-target="#my-menu-dropdown">
<button class="ink-button">Dropdown</button>
<ul id="my-menu-dropdown" class="dropdown-menu">
<li class="heading">I am a heading</li>
<li class="separator-above"><a href="#">Option</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Option</a></li>
<li class="separator-above disabled"><a href="#">Disabled option</a></li>
</ul>
</div>Dismiss automatically when mouse moves away.
By adding the data-dismiss-after="<s>" option, the Dropdown will go away automatically after s seconds pass.
Here we hide it after 2 seconds.
Demo
Code
<div class="ink-dropdown" data-target="#my-menu-dropdown-2" data-dismiss-after="2">
<button class="ink-button">Dropdown</button>
<ul id="my-menu-dropdown-2" class="dropdown-menu">
<li class="disabled"><a href="#">Disabled option</a></li>
</ul>
</div>Dropdown options
data-target="#my-menu"- Make#my-menutheulwhich this Dropdown opens.data-hover-open="<seconds>"- The number of seconds you need to hover with the mouse before the dropdown opens.data-dismiss-after="<seconds>"- When the mouse moves away from the dropdown, wait forsecondsseconds and then dismiss.data-dismiss-on-inside-click="true"- Dismiss the dropdown when there’s a click inside.data-dismiss-on-outside-click="false"- Do not dismiss the dropdown when there’s a click outside.
Advanced Dropdown stuff:
You can visit the Dropdown API docs to find out about Javascript-only options, javascript methods, and how to create Dropdowns using Javascript
Droppable
The Droppable is a dropping area for Draggables. It’s useful to create shopping carts, playlists, and other things which rely on dragging and dropping action.
Droppable Examples
Simple Droppables
Let’s drag a couple of Draggables into a droppable!
Demo
A droppable
A couple of draggables
Code
<p>A droppable</p>
<ul class="ink-droppable droppable-2" data-on-drop="move">
</ul>
<p>A couple of draggables</p>
<li class="ink-label ink-draggable blue">Draggable 1</li>
<li class="ink-label ink-draggable green">Draggable 2</li>
<li class="ink-label ink-draggable orange">Draggable 3</li>Acceptance
You can choose what Draggables get dropped in your droppable! Here we see only green Draggables accepted in a Droppable.
Demo
Drop only green things here:
A couple of draggables
Code
<p>Drop only green things here:</p>
<ul class="ink-droppable droppable-1" data-accept=".green" data-on-drop="move">
</ul>
<p>A couple of draggables</p>
<li class="ink-label ink-draggable green">Draggable 1</li>
<li class="ink-label ink-draggable green">Draggable 2</li>
<li class="ink-label ink-draggable red">Draggable 3</li>Droppable options
data-hover-class="hoverin"- Add the.hoverinclass when a Draggable and hovering this droppable.data-accept=".only-these-draggables"- Accept only elements with the class.only-these-draggables.
Drop behaviour options
These options can be further customized using javascript. Without javascript, though, there are already a few pre-made actions.
These actions are "move" and "copy", which move or copy the draggable element into this draggable, or "revert", which puts the draggable right back where it came from..
data-on-drop="<move copy or revert>"- When an element is dropped, move or copy it here, or revert it to where it came from.data-on-hover="<move copy or revert>"- When an element is hovering the droppable, move or copy it here, or revert it to where it came from.data-on-drop-out="<move copy or revert>"- When a Draggable is dropped outside of this droppable, move or copy it here, or revert it to where it came from.
Advanced Droppable stuff:
You can visit the Droppable API docs to find out about Javascript-only options, javascript methods, and how to create Droppables using Javascript
FormValidator_2
FormValidator is a component which validates forms interactively on the client side before any data is sent to the server. By doing this, it provides a less waiting time, and a better experience to the user.
To use FormValidator, add the .ink-formvalidator class to a <form> element. Ink won’t let the user submit until the data is valid.
You will probably need to read the Forms UI Element documentation to get to grips with the classes used. TL;DR: .ink-form goes outside, .control-group is nestable and groups similar controls, and .control wraps the inputs.
FormValidator_2 Examples
Basic example
Here is a simple example of a user registration field:
Demo
Note: The required class is related to the Form UI Element. it doesn’t affect the FormValidator’s behaviour.
Code
<form class="ink-form ink-formvalidator" method="post" action="#">
<div class="control-group required">
<label for="name">Name:</label>
<div class="control">
<input type="text" data-rules="required|text[true,false]" name="name" id="name" />
</div>
</div>
<div class="control-group required">
<label for="e-mail">Email:</label>
<div class="control">
<input type="text" name="e-mail" id="e-mail" data-rules="required|email" />
</div>
</div>
<div class="control-group required">
<label for="pass">Password: </label>
<div class="control">
<input type="password" name="password" id="pass" data-rules="required|min_length[8]" />
</div>
</div>
<div class="control-group required">
<label for="confpass">Confirm Password:</label>
<div class="control">
<input type="password" name="confpass" id="confpass" data-rules="matches[password]" data-label="password confirmation" />
</div>
</div>
<input type="submit" name="sub" value="Submit" class="ink-button success" />
</form>Required radio buttons and checkboxes
Here’s how FormValidator deals with <input type="radio"> and <input type="checkbox"> inputs.
Demo
Note: The required class is related to the Form UI Element. it doesn’t affect the FormValidator’s behaviour.
Code
<form class="ink-form ink-formvalidator column-group" method="post" action="#">
<div class="all-50 small-100 tiny-100">
<div class="control-group required">
<p class="label">An offer you cannot refuse.</p>
<ul class="control unstyled">
<li>
<input type="radio" name="accept-offer" id="accept-offer-id" value="1" data-rules="required" data-label="Accept Offer" />
<label for="accept-offer-id">Okay!</label>
</li>
<li>
<input type="radio" name="accept-offer" id="refuse-offer-id" value="2" />
<label for="refuse-offer-id">No, thanks.</label>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
<div class="all-50 small-100 tiny-100">
<div class="control-group required">
<p class="label">Here's a box you must absolutely check.</p>
<ul class="control unstyled">
<li>
<input type="checkbox" name="accept-tos" id="accept-tos-id" value="1" data-rules="required" data-label="Accept the TOS" />
<label for="accept-tos-id">I accept the Terms of Service of this website.</label>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
<input type="submit" name="sub" value="Submit" class="ink-button success" />
</form>Custom error message strings
To issue a custom error message for that input, add a data-error attribute to the element
Demo
Note: The required class is related to the Form UI Element. it doesn’t affect the FormValidator’s behaviour.
Code
<form class="ink-form ink-formvalidator column-group" method="post" action="#">
<div class="all-50 small-100 tiny-100">
<div class="control-group required">
<p class="label">An offer you cannot refuse.</p>
<ul class="control unstyled">
<li>
<input type="radio" name="accept-offer" id="accept-offer-2-id" value="1" data-rules="required" data-label="Accept Offer" data-error="You messing with me?" />
<label for="accept-offer-2-id">Okay!</label>
</li>
<li>
<input type="radio" name="accept-offer" id="refuse-offer-2-id" value="2" />
<label for="refuse-offer-2-id">No, thanks.</label>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
<input type="submit" name="sub" value="Submit" class="ink-button success" />
</form>FormValidator_2 options for the form
Put this in your <form> if you want to translate the form. Options to define the validation of each input are below.
data-lang="pt_PT"- Write error messages in portuguese. Languages available arept_PTanden_USbut others can be added through javascript.
FormValidator_2 options for each input
After adding the .ink-formvalidator class to your FormValidator, add these data-attributes to your form inputs (input, select, textarea…) to configure how they are validated.
Each field (<input>, <select>, <textarea>, etc.) which you want to validate in your form needs to have “rules”. These rules define what can go and what can’t go on this element. Read more on them in “Validation rules”, below.
data-rules="Field name in human-readable form"- Rules for this field. Read more in the “Validation rules” section, below.data-label="Field name text"- The name of this field. It is used to show in error messages. By default the label is thenameattribute of your field.
Validation rules
This is what you put in data-rules for each element. Here are a few examples of what you can do:
data-rules="required"- Must be filled in.data-rules="alpha"- Just alphabetic characters (A to Z), lower case or upper case.data-rules="alpha_numeric"- Likealphabut accepts numbers too!data-rules="credit_card"- A credit card number.data-rules="email"- A valid e-mail.data-rules="range[0,10]"- Numbers (not exactly integers) between 0 and 10.data-rules="numeric[.]"- A numeric field, using the.as a decimal separator. (Ex: “1.5”)data-rules="numeric[.,2]"- A numeric field with at most 2 decimal places. (“1.23” is okay but “1.234” is not)data-rules="numeric[.,2,4]"- A numeric field with at most 2 decimal places and at most 4 digits on the left. (“1234.56” is okay but “12345.6” and “1234.567” are not)data-rules="integer"- Only whole numbers.
You can combine these rules, like this:
data-rules="required|number"- A required number.data-rules="required|email"- A required email.data-rules="integer|range[0,10]"- A whole number between 0 and 10.
Some assorted rules which are useful in combination with other rules:
data-rules="min_length[4]"- Must have at least 4 characters.data-rules="max_length[4]"- Can’t have more than 4 characters.data-rules="exact_length[4]"- Must have exactly 4 characters.
Random rules you might need:
data-rules="color"- A color in#hex,rgb(),rgba(),hsl(),hsla()format.data-rules="date[<format>]"- A date.formatis a date format string in the syntax of PHP’sdate()functiondata-rules="decimal[...]"- Exactly likenumericbut only decimal numbers are allowed.data-rules="ip[ipv6]"- An IP address.data-rules="ip[ipv4]"- A legacy IP address.data-rules="phone[PT]"- A Portuguese phone number.data-rules="phone[CV]"- A Cape Verde phone number.data-rules="phone[AO]"- An Angolan phone number.data-rules="phone[MZ]"- A Mozambique phone number.data-rules="phone[TL]"- A Timor phone number.data-rules="phone"- Any of the above types of phone number.data-rules="url"- A URL. (Ex:"/foo/bar","https://example.com/foo/bar", etc.)data-rules="url[true]"- Just likeurlbut only if it contains the “https://” part.data-rules="ean"- A barcode in EAN-13 format.
You can see more validation rules, as well as a more in-depth description of each one of them, in the JS documentation for FormValidator.validationFunctions
Advanced FormValidator_2 stuff:
You can visit the FormValidator_2 API docs to find out about Javascript-only options, javascript methods, and how to use FormValidator using Javascript.
LazyLoad
LazyLoad delays the downloading of images, showing them only when they get to the viewport. This is useful in optimizing image-heavy websites.
You can use the more advanced Javascript API to load things other than images, such as widgets, videos, active content, etc.
While the images are loading or offscreen, their appearance will be a simple, more lightweight, placeholder. You can define what this placeholder using the data-placeholder option of the LazyLoad, about which you can learn about below, in “LazyLoad options for the container”.
A LazyLoad is comprised of a container element, which can be the <body> if you like, with the class .ink-lazyload, and LazyLoad items, with the class .lazyload-item, and with a data-src attribute instead of a src attribute.
It is recommended that you make sure, using CSS, that the images will take as much space after they loaded as before loading. In other words, reserve space for your images! This avoids weird scrolling issues.
LazyLoad Examples
Load a few images
The images below will only load when you scroll
Demo
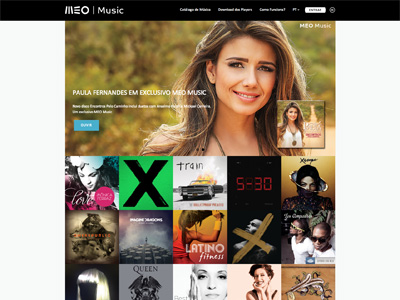


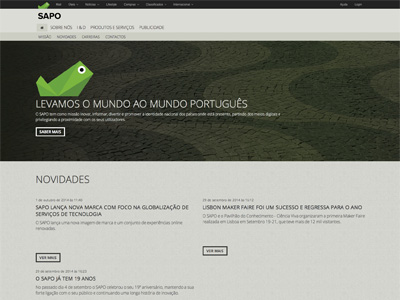

Code
<!-- the "data-delta" below is just so you can see the effect in the demo -->
<div class="ink-lazyload" data-delta="-150" data-placeholder="/assets/img/loading.gif">
<p><img class="lazyload-item my-lazyloaded-image" data-src="/assets/img/meomusic.jpg"></p>
<p><img class="lazyload-item my-lazyloaded-image" data-src="/assets/img/pessoa.jpg"></p>
<p><img class="lazyload-item my-lazyloaded-image" data-src="/assets/img/codebits.jpg"></p>
<p><img class="lazyload-item my-lazyloaded-image" data-src="/assets/img/sobre.jpg"></p>
<p><img class="lazyload-item my-lazyloaded-image" data-src="/assets/img/videos.jpg"></p>
</div>
<style>
.ink-lazyload .my-lazyloaded-image {
height: 180px; /* Reserve height to avoid weird scrolling issues */
width: auto;
}
</style>Add a CSS class to loaded images
When images are loaded, they will get a new CSS class and have a pretty fade-in!
Demo


Code
<!-- the "data-delta" below is just so you can see the effect in the demo -->
<div class="ink-lazyload" data-delta="-150" data-placeholder="/assets/img/loading.gif" data-loaded-class="loaded">
<p><img class="lazyload-item loaded-class-example" data-src="/assets/img/meomusic.jpg"></p>
<p><img class="lazyload-item loaded-class-example" data-src="/assets/img/pessoa.jpg"></p>
</div>
<style>
.ink-lazyload .loaded-class-example {
height: 180px; /* Reserve height to avoid weird scrolling issues */
width: auto;
transition: opacity 2s ease;
opacity: 0.2;
}
.ink-lazyload .loaded-class-example.loaded {
opacity: 1;
}
</style>LazyLoad options for each lazily loaded item
data-src="/my/image.png"- The real source of the image, only loaded when the image is on screen.
LazyLoad options for the container
data-placeholder="/my-loading-spinner.gif"- Placeholder value for items which are not ‘visible’, in case they don’t already have a value set.data-loaded-class="loaded"- Add the “loaded” class to the images when they’re loaded.data-delta="100"- Start loading the images 100px before they are on the screen.data-delta="-100"- Start loading the images 100px after they are on the screen.data-delay="1000"- Wait 1000 milliseconds (1 second) before showing the image.data-item=".my-crazy-selector"- Find images by.my-crazy-selectorinstead of finding images with the.lazyload-itemclass.
Advanced LazyLoad stuff:
You can visit the LazyLoad API docs to find out about Javascript-only options, javascript methods, and how to use LazyLoaders with Javascript. There’s more advanced stuff that isn’t covered here, like loading non-image elements with callbacks.
Modal
The Modal component allows you to overlay something on the entire page, possibly an error message that refers to the whole page, or a follow-up form or dialog to a submission process.
It works by putting a shade element with position:fixed covering the entire viewport and avoiding accidental interaction with the rest of the page, and placing a modal element on the center of the screen using javascript.
It plays well with the .ink-dismiss class (the Close element). An element with the ink-dismiss class dismisses the modal that contains it.
Modal Examples
Open a simple modal
Click the button to open a modal
Demo
Code
<div class="ink-shade fade">
<div id="myModal" class="ink-modal fade" data-trigger="#myModalTrigger1" data-width="80%" data-height="80%" role="dialog" aria-hidden="true" aria-labelled-by="modal-title">
<div class="modal-body" id="modalContent">
<h3>This is the modal content</h3>
<figure class="ink-image">
<img src="https://lorempixel.com/1200/675/sports/1" alt="" class="ink-image">
</figure>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<a href="#" id="myModalTrigger1" class="ink-button">Open example modal</a>A modal with a dismiss button, header, footer
Besides the content, this modal has a dismiss button, a header and a footer, besides the content.
Demo
Code
<div class="ink-shade fade">
<div id="myModal" class="ink-modal fade" data-trigger="#myModalTrigger2" data-width="80%" data-height="80%" role="dialog" aria-hidden="true" aria-labelled-by="modal-title">
<div class="modal-header">
<button class="modal-close ink-dismiss"></button>
<h2 id="modal-title">This is the modal header</h2>
</div>
<div class="modal-body" id="modalContent">
<h3>This is the modal content</h3>
<figure class="ink-image">
<img src="https://lorempixel.com/1200/675/sports/1" alt="" class="ink-image">
</figure>
</div>
<div class="modal-footer">
<div class="push-right">
<!-- Anything with the ink-dismiss class will close the modal -->
<button class="ink-button caution ink-dismiss">Close</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<a href="#" id="myModalTrigger2" class="ink-button">Open example modal</a>An automatically opened modal
To automatically open the modal, just omit the trigger!
Demo
Code
<div class="ink-shade fade">
<div id="myModal" class="ink-modal fade" data-width="80%" data-height="80%" role="dialog" aria-hidden="true" aria-labelled-by="modal-title">
<div class="modal-body" id="modalContent">
<h3>This is the modal content</h3>
<figure class="ink-image">
<img src="https://lorempixel.com/1200/675/sports/1" alt="" class="ink-image">
</figure>
</div>
</div>
</div>Modal options
data-trigger="#my-button"- The modal will open when#my-buttonis clicked.data-width="600px"- Make the modal 600px wide.data-height="400px"- Make the modal 400px tall.data-width="40%"- Make the modal width be 40% of the screen width.data-height="20%"- Make the modal’s height be 20% of the screen height.data-auto-display="true"- Displays the Modal automatically when constructed.data-close-on-click="false"- Don’t close when the user clicks outside the modal.data-close-on-escape="false"- Don’t close the modal when ESC is pressed.data-responsive="false"- Don’t resize the modal when the screen is resized.
Advanced Modal stuff:
You can visit the Modal API docs to find out about Javascript-only options, javascript methods, and how to use Modals with Javascript and subscribe to their events.
Pagination
You can use Pagination when you need interactive paginators. It does not paginate anything by itself and must be connected to some other piece of javascript to do anything useful. Above you see it used together with Carousel to change its pages.
It uses the CSS you see in the Pagination UI Element (CSS). If you want a static pagination, just use that. If you really want a dynamic pagination, read on.
Pagination Examples
Simple pagination
Here we use the data-size option to tell Pagination how many pages it is paginating.
Demo
Code
<nav class="ink-navigation" id="myPagination1" data-size="5">
<ul class="pagination black"></ul>
</nav>Lots of pages!
This example shows you how to deal with showing 100 pages without having all the numbers 1, 2, 3, 4... 100 written down.
This is effectively the Pagination paginating itself :)
Demo
Code
<nav class="ink-navigation" id="myPagination2" data-size="100" data-max-size="5">
<ul class="pagination red"></ul>
</nav>Pagination options
Page count
You can define the page count in two ways. One of them is just saying how many pages you have. The other is by telling it how many items you have, and how many items per page you need. Pagination will do the math for you in this case and calculate the page count by itself.
Here is how you define the page count directly:
data-size="<size>"- Define the page count to besize, directly.
Here’s how you tell Pagination to do the math for you:
data-total-item-count="<item_count>"- Tell Pagination you haveitem_countitems (don’t forget the below option too!).data-items-per-page="<per_page>"- Tell Pagination you plan to displayper_pageitems per page.
Options for dealing with large amounts of pages
data-max-size="<max>"- Show at mostmaxnumbers. This enables the “Next N”, “Previous N” buttons.data-previous-page-class="<class>"- Addclassto the “previous N” button.data-next-page-class="<class>"- Addclassto the “next N” button.
Presentation options:
data-first-label="<text>"- Writetexton the first page button instead of ‘First’.data-last-label="<text>"- Writetexton the last page button instead of ‘Last’.data-previous-label="<text>"- Writetexton the previous button instead of ‘Previous’-data-next-label="<text>"- Writetexton the next button instead of ‘Next’data-previous-page-label="<text>"- Writetexton the previous page button instead of ‘Previous {Items per page}’.data-next-page-label="<text>"- Writetexton the next page button instead of ‘Next {Items per page}’.data-pagination-class="<class>- Class for the pagination elementdata-active-class="<class>- Class that marks page as active (current page number)data-disabled-class="<class>- Class that marks a page as disableddata-previous-class="<class>- Class for the “previous” elementdata-next-class="<class>- Class for the “next” elemntdata-hide-class="<class>- Class which hides elements
Misc options:
data-start="3"- Start in page 3 instead of page 1.data-side-buttons="false"- Hide the first, last, previous, next, “previous N” and “next N” buttons. Do not use together withdata-max-size.data-auto-wrap="true"- Navigate to first page when clicking “next” in the last page and vice-versa.data-parent-tag- HTML Tag used as the parent node.data-child-tag- HTML Tag used as the child nodes.
Advanced Pagination stuff:
You can visit the Pagination API docs to find out about Javascript-only options, javascript methods, and how to use Paginations with Javascript and subscribe to their events.
ProgressBar
A ProgressBar can be used to indicate progress in a certain process.
ProgressBar Example
This is a progress bar. The process is well under way, it seems, at 70%.
Demo
Code
<div class="ink-progress-bar" data-start-value="70">
<span class="caption">I am a grey progress bar</span>
<div class="bar grey"></div>
</div>ProgressBar options
Use this vast array of options to customize your ProgressBar:
data-start-value="20"- Start at 20% instead of 0%.
You can also use some color classes (instead of grey) to color your progress bar.
Advanced ProgressBar stuff:
You can visit the ProgressBar API docs to learn how to create ProgressBars with javascript and manipulate them in real time.
SmoothScroller
SmoothScroller is a component for
SmoothScroller Examples
Basic usage
This shows you how to set a couple of anchor links which, when clicked, scroll smoothly up to their destination. Here are two links and sections:
Demo
[lots and lots of content...]
...
Part 1
Part 1 content
Part 2
Part 2 content
Code
<nav>
<a href="#part1" class="ink-smooth-scroll">Scroll to "Part 1"</a>
<a href="#part2" class="ink-smooth-scroll">Scroll to "Part 2"</a>
</nav>
<p>[lots and lots of content...]</p>
<p>...</p>
<section id="part1">
<h1>Part 1</h1>
<p>Part 1 content</p>
</section>
<section id="part2">
<h1>Part 2</h1>
<p>Part 2 content</p>
</section>Leaving a margin
This example shows the use of data-margin to scroll up to 200px above the target.
The data-margin option is very useful if you have a position:fixed menu or top bar on the top of your page. Using it avoids hiding important content behind that bar.
Demo
[lots and lots of content...]
...
I am something!
Code
<nav>
<a href="#something" class="ink-smooth-scroll" data-margin="200">Scroll to 200px above "something"!</a>
</nav>
<p>[lots and lots of content...]</p>
<p>...</p>
<p id="something">I am <strong>something</strong>!</p>Scrolling really fast
Here is how you use data-speed to scroll really fast. It defaults to "10". Smaller is faster, larger is slower.
Demo
[lots and lots of content...]
...
Thing 1
Thing 1 fast!
Thing 2
Thing 2 fast!
Code
<nav>
<a href="#thing-1-fast" class="ink-smooth-scroll" data-speed="2">
Scroll really fast to "Thing 1"
</a>
<a href="#thing-2-fast" class="ink-smooth-scroll" data-speed="2">
Scroll really fast to "Thing 2"
</a>
</nav>
<p>[lots and lots of content...]</p>
<p>...</p>
<h1 id="thing-1-fast">Thing 1</h1>
<p>Thing 1 fast!</p>
<h1 id="thing-2-fast">Thing 2</h1>
<p>Thing 2 fast!</p>SmoothScroller options
When a link is clicked, it is checked for several things:
href="#my-item-id"- Scroll up to the element with IDmy-item-id. Only works with IDs, just like regular anchor links.data-margin="42"- When scrolling, leave a 42px margin above the target. Useful if you have a 42px-tallposition:fixedtop bar.data-speed="5"- Scroll faster.data-speed="20"- Scroll slower.data-change-hash="false"- Don’t change the URL hash (#hash), just scroll there.
Advanced SmoothScroller stuff:
You can visit the SmoothScroller API docs to find out about Javascript-only options, javascript methods, and how to use SmoothScrollers with Javascript and subscribe to their events.
SortableList
SortableList turns a list into a list which can be sorted by the user using the mouse. It does not currently work with touch events.
A handle can be selected, in which case the user will only be able to drag the list items by that handle (something like a “drag here” icon). SortableList can also be used to sort non-list elements.
SortableList Examples
Simple sorting
Let’s sort a few items:
Demo
- First
- Second
- Third
Code
<ul class="unstyled ink-sortable-list">
<li>First</li>
<li>Second</li>
<li>Third</li>
</ul>Styling the dragged item
While you’re dragging, the dragged item gets the “placeholder” CSS class, enabling you to style it as you like.
Demo
- First
- Second
- Third
Code
<ul class="unstyled styled-placeholder ink-sortable-list">
<li>First</li>
<li>Second</li>
<li>Third</li>
</ul>
<style>
.styled-placeholder .placeholder {
box-shadow: 1px 1px 4px black
}
</style>Styling something else
SortableList will also add the drag class to the <html> element while
you sort things. You can change it to another class using data-dragging-class.
Demo
- First
- Second
- Third
Code
<ul class="unstyled ink-sortable-list" data-dragging-class="make-visible">
<li>First</li>
<li>Second</li>
<li>Third</li>
</ul>
<div class="invisible-until-you-drag">
<i class="fa fa-check"></i> Hey! I see you're dragging things! Welcome to Ink!
</div>
<style>
.invisible-until-you-drag {
visibility: hidden;
}
.make-visible .invisible-until-you-drag {
visibility: visible;
color: green;
}
</style>Sorting by a handle
In this example, you can only drag by the “bars” icon to the left of each word.
Demo
- First
- Second
- Third
Code
<ul class="unstyled ink-sortable-list" data-handle-selector=".drag-here">
<li><span class="drag-here fa fa-bars" title="Drag here"></span> First</li>
<li><span class="drag-here fa fa-bars" title="Drag here"></span> Second</li>
<li><span class="drag-here fa fa-bars" title="Drag here"></span> Third</li>
</ul>Sorting non-list elements
Here’s a sortable table. Notice that we use data-drag-selector="tbody tr", to
tell SortableList what is being sorted is the rows inside the <tbody> element.
Demo
| Name | Number |
|---|---|
| First | 1 |
| Second | 2 |
| Third | 3 |
Code
<table class="ink-table ink-sortable-list" data-drag-selector="tbody tr">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Number</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr><td>First</td><td>1</td></tr>
<tr><td>Second</td><td>2</td></tr>
<tr><td>Third</td><td>3</td></tr>
</tbody>
</table>Sorting a grid of things instead of a list of things
Below you can see two sortable grids, just to show off two ways of sorting items.
When “swap mode” is active, the sorting makes more sense in grids, although it changes the list around a lot.
Demo
List mode:
- First
- Second
- Third
- Fourth
Swap mode:
- First
- Second
- Third
- Fourth
Code
<h3>List mode:</h3>
<ul class="unstyled clearfix ink-sortable-list">
<li class="all-50 push-left">First</li>
<li class="all-50 push-left">Second</li>
<li class="all-50 push-left">Third</li>
<li class="all-50 push-left">Fourth</li>
</ul>
<h3>Swap mode:</h3>
<ul class="unstyled clearfix ink-sortable-list" data-swap="true">
<li class="all-50 push-left">First</li>
<li class="all-50 push-left">Second</li>
<li class="all-50 push-left">Third</li>
<li class="all-50 push-left">Fourth</li>
</ul>SortableList options
These options help you configure SortableList. Most of them have a working example above.
data-placeholder-class="my-placeholder"- Add themy-placeholderclass to the dragged placeholder. By default theplaceholderclass is added.data-dragging-class="html-element-with-things-being-dragged"- Add this class to the<html>element when something is dragged. By default, thedraggingclass is added.data-drag-selector=".my-dragged-items"- Sort.my-dragged-itemsinstead oflielements. You see this in use above in “Sorting non-list elements”.data-handle-selector=".handle"- Drag nodes by a handle, marked by the.handleclass. This handle must be inside the dragged node.data-swap="true"- Instead of reordering items, swap them. Makes a lot of sense when sorting grids, but does nothing in simple lists.data-cancel-mouse-out="true"- Stop dragging if the mouse leaves the container.
Advanced SortableList stuff:
You can visit the SortableList API docs to find out about Javascript-only options, javascript methods, and how to use SortableLists with Javascript.
Spy
Spy is a simple way to help the user keep track of where they are when scrolling your page.
As a user scrolls down the page and changes to new sections (they may be actual
<section> elements or whatever you like), Spy will highlight the corresponding
link on your menu. This is useful when your menu has position:fixed and has a
bunch of anchor links to several parts of the page.
Your menu must have all links inside li tags. These will get the .active
class. You then style the .active class as you like.
Spy Examples
Basic example
A bunch of sections
Demo
Code
<nav class="ink-navigation" id="my-menu">
<ul class="menu horizontal black">
<li><a href="#my-section-1">Water</a></li>
<li><a href="#my-section-2">Bones</a></li>
<li><a href="#my-section-3">Pilot</a></li>
</ul>
</nav>
<div class="ink-grid my-sections">
<section id="my-section-1" data-spy="true" data-target="#my-menu">
<h2>Water</h2>
<p>
You think water moves fast? You should see ice. It moves like it has a mind. Like it knows it killed the world once and got a taste for murder. After the avalanche, it took us a week to climb out. Now, I don't know exactly when we turned on each other, but I know that seven of us survived the slide... and only five made it out.
</p>
<p>Now we took an oath, that I'm breaking now. We said we'd say it was the snow that killed the other two, but it wasn't. Nature is lethal but it doesn't hold a candle to man.</p>
</section>
<section id="my-section-2" data-spy="true" data-target="#my-menu">
<h2>Bones</h2>
<p>
Your bones don't break, mine do. That's clear. Your cells react to bacteria and viruses differently than mine. You don't get sick, I do. That's also clear. But for some reason, you and I react the exact same way to water. We swallow it too fast, we choke. We get some in our lungs, we drown. However unreal it may seem, we are connected, you and I. We're on the same curve, just on opposite ends.
</p>
</section>
<section id="my-section-3" data-spy="true" data-target="#my-menu">
<h2>Pilot</h2>
<p>
Well, the way they make shows is, they make one show. That show's called a pilot. Then they show that show to the people who make shows, and on the strength of that one show they decide if they're going to make more shows. Some pilots get picked and become television programs. Some don't, become nothing. She starred in one of the ones that became nothing.
</p>
</section>
<p>...</p>
<p>...</p>
</div>
<style>
#my-menu .active {
background: #333 !important;
color: yellow;
}
</style>Spy options
There’s only one option to Spy.
data-target="#the-target"- Make#the-targetthe spy target.
Advanced Spy stuff:
You can visit the Spy API docs to find out about Javascript-only options, javascript methods, and how to create Spies using Javascript
Stacker
Stacker will reorganize N columns when the screen is not wide enough to show them all. It will mash together the contents of the 3 columns
It does so to avoid the problem of the elements’ unknown height
Stacker Examples
3 feeds example
This example re-stacks 3 feeds of data in the large viewport into a single column in the small viewport. Resize your viewport and watch the items get mashed together.
Demo
Code
<div class="column-group ink-stacker gutters">
<div class="all-33 medium-50 small-100 tiny-100 stacker-column">
<div class="ink-alert basic success stacker-item"><b>A - 1</b></div>
<div class="ink-alert basic success stacker-item bit-taller"><b>A - 2</b></div>
<div class="ink-alert basic success stacker-item"><b>A - 3</b></div>
</div>
<div class="all-33 medium-50 small-100 tiny-100 hide-small stacker-column">
<div class="ink-alert basic warning stacker-item"><b>B - 1</b></div>
<div class="ink-alert basic warning stacker-item"><b>B - 2</b></div>
<div class="ink-alert basic warning stacker-item bit-taller"><b>B - 3</b></div>
</div>
<div class="all-33 medium-50 small-100 tiny-100 hide-medium hide-small stacker-column">
<div class="ink-alert basic info stacker-item"><b>C - 1</b></div>
<div class="ink-alert basic info stacker-item"><b>C - 2</b></div>
<div class="ink-alert basic info stacker-item"><b>C - 3</b></div>
</div>
</div>Items with multiple heights
This example shows off Stacker’s capacity to deal with multiple height items even as the screen width forces it to reduce the amount of columns. It contrasts a “classic” way to do things with the “Stacker” way to achieve a similar result.
Demo
Without stacker:
With stacker:
Code
<h4>Without stacker:</h4>
<div class="column-group gutters column-group stacker-example-heights no-stacker">
<div class="xlarge-33 large-33 medium-50 small-100 tiny-100">
<div class="all-100 ink-alert basic"><b>a</b></div>
</div>
<div class="xlarge-33 large-33 medium-50 small-100 tiny-100">
<div class="all-100 ink-alert basic bit-taller"><b>b</b></div>
</div>
<div class="xlarge-33 large-33 medium-50 small-100 tiny-100">
<div class="all-100 ink-alert basic really-tall"><b>c</b></div>
</div>
<div class="xlarge-33 large-33 medium-50 small-100 tiny-100">
<div class="all-100 ink-alert basic bit-taller"><b>d</b></div>
</div>
<div class="xlarge-33 large-33 medium-50 small-100 tiny-100">
<div class="all-100 ink-alert basic"><b>e</b></div>
</div>
<div class="xlarge-33 large-33 medium-50 small-100 tiny-100">
<div class="all-100 ink-alert basic bit-taller"><b>f</b></div>
</div>
<div class="xlarge-33 large-33 medium-50 small-100 tiny-100">
<div class="all-100 ink-alert basic really-tall"><b>g</b></div>
</div>
<div class="xlarge-33 large-33 medium-50 small-100 tiny-100">
<div class="all-100 ink-alert basic "><b>h</b></div>
</div>
<div class="xlarge-33 large-33 medium-50 small-100 tiny-100">
<div class="all-100 ink-alert basic "><b>i</b></div>
</div>
</div>
<h4>With stacker:</h4>
<div class="column-group ink-stacker gutters stacker-example-heights">
<div class="all-33 medium-50 small-100 tiny-100 stacker-column">
<div class="ink-alert basic stacker-item"><b>a</b></div>
<div class="ink-alert basic stacker-item bit-taller"><b>d</b></div>
<div class="ink-alert basic stacker-item really-tall"><b>g</b></div>
</div>
<div class="all-33 medium-50 small-100 tiny-100 hide-small stacker-column">
<div class="ink-alert basic stacker-item bit-taller"><b>b</b></div>
<div class="ink-alert basic stacker-item"><b>e</b></div>
<div class="ink-alert basic stacker-item bit-taller"><b>h</b></div>
</div>
<div class="all-33 medium-50 small-100 tiny-100 hide-medium hide-small stacker-column">
<div class="ink-alert basic stacker-item really-tall"><b>c</b></div>
<div class="ink-alert basic stacker-item"><b>f</b></div>
<div class="ink-alert basic stacker-item"><b>i</b></div>
</div>
</div>
<style>
.stacker-example-heights .bit-taller {
height: 5.5em;
}
.stacker-example-heights .really-tall {
height: 8em;
}
.no-stacker.stacker-example-heights .ink-alert {
margin: 0; /* Just a small hack because we had to change the DOM structure a little bit. */
}
.no-stacker.stacker-example-heights > div {
margin-bottom: 1em; /* Just a small hack because we had to change the DOM structure a little bit. (part 2) */
}
</style>Stacker options
data-large-cols="5"- Have 5 columns in the large viewport instead of 3.data-medium-cols="3"- Have 3 column in the medium viewport instead of 3.data-small-cols="2"- Have 2 columns in the small viewport instead of 1.data-item=".my-stacker-item” - Your stacker items. This defaults to.stacker-item.data-column=".my-stacker-columns"- If for some reason you don’t want to use thestacker-columnclass to identify your stacker columns, you can use this option to change it.data-is-ordered="false"- Don’t reorder the stacks when resizing.
Advanced Stacker stuff:
You can visit the Stacker API docs to find out about Javascript-only options, javascript methods, and how to create Stackers using Javascript
Sticky
Sticky Examples
Simple sticky
Here is sticky’s default behavior. No options, sticking an alert to the top of the screen.
Demo
Code
<h1>Welcome to my website</h1>
<div class="ink-sticky">
<div class="ink-alert basic">Hey I stick to the top when you scroll!</div>
</div>
<p>Content goes here...</p>
<p>Content goes here...</p>
<p>Content goes here...</p>
<p>Content goes here...</p>
<p>Content goes here...</p>
<p>Content goes here...</p>
<style>
.ink-sticky .ink-alert {
/* Remove the ink-alert's margins to keep it really on the top of the screen */
margin: 0;
}
</style>Styling the sticky different when it’s “stuck”
When a sticky is stuck to the top of the screen, it gets the .ink-sticky-stuck class. You can use that to style your sticky differently when it’s stuck!
Demo
Code
<h1>Welcome to my website</h1>
<div class="ink-sticky">
<div class="ink-alert basic">Hey I turn red when you scroll!</div>
</div>
<p>Content goes here...</p>
<p>Content goes here...</p>
<p>Content goes here...</p>
<p>Content goes here...</p>
<p>Content goes here...</p>
<p>Content goes here...</p>
<style>
.ink-sticky.ink-sticky-stuck .ink-alert {
color: red;
background: #FFAEAB /* some kind of red */;
border-color: red;
}
.ink-sticky .ink-alert {
/* Remove the ink-alert's margins to keep it really on the top of the screen */
margin: 0;
}
</style>data-bottom-element tells Sticky to avoid going below a certain element
This option is very useful for large footers, which don’t play well with sticky elements hovering on top of them.
It also works well when the Sticky only refers to a section and you wouldn’t want it flying off of it because that would be confusing.
Just add data-bottom-element="#bottom-element and Sticky will avoid going below that element.
Demo
Code
<div class="ink-sticky" data-bottom-element=".stop-here">
<div class="ink-alert basic">Hey I can stick to the top!</div>
</div>
<p>Content goes here...</p>
<p>Content goes here...</p>
<p>Sticky stops <span class="ink-label stop-here">here</span></p>
<p>Content goes here...</p>
<p>Content goes here...</p>
<p>Content goes here...</p>
<style>
.ink-sticky .ink-alert {
/* Remove the ink-alert's margins to keep it really on the top of the screen */
margin: 0;
}
</style>Sticky options
data-top-element="#top-element"- Don’t let the sticky go above or run into this element.data-bottom-element="#bottom-element"- Don’t let the sticky go below or run into this element.data-offset-top="20px"- Instead of sticking right to the top of the screen, keep a margin of 20px. This is very, very useful, if you already have aposition:fixedtop bar on your page.data-offset-bottom="10px"- Likedata-offset-top, but for the bottom. Avoids the sticky sticking right to the bottom of the screen.data-inline-dimensions="false"- Tell sticky to not mess with your element’sstyleto set dimensions. You may want to do this because you want to set the dimensions yourself in your CSS for.ink-stickyor.ink-sticky-stuck.data-inline-position="false"- Tell sticky to not mess with your element’sstyleto set position. You may want to do this because you want to set the position yourself in your CSS for.ink-stickyor.ink-sticky-stuck.data-wrapper-class="my-wrapper"- Add this class to the sticky wrapper (the DIV that stands in place for the element when it is put inposition:fixed).data-sticky-class="i-am-stuck"- Add this class to the sticky when it’s stuck (position:fixed) on the top or bottom of the screen.
Advanced Sticky stuff:
You can visit the Sticky API docs to find out about Javascript-only options, javascript methods, and how to create Stickies using Javascript
Tabs
The Tabs Component offers a simple way to build a tab-separated layout, allowing you to offer multiple content panes in the same space with intuitive navigation. This component requires your markup to have:
- A container element with everything below:
- An element with the
.tabs-navclass, containing links with the[href]attribute set to the ID of the section they point at. Like regular in-document anchor links. - Your section elements with the corresponding id attributes and the
.tabs-contentclass.
- An element with the
Tabs examples
Simple Tabs
A simple Tabs component, with tabs on top and two sections.
Demo
Home
A home is a dwelling-place used as a permanent or semi-permanent residence for an individual, family, household or several families in a tribe. It is often a house, apartment, or other building, or alternatively a mobile home, houseboat, yurt or any other portable shelter. Larger groups may live in a nursing home, children's home, convent or any similar institution. A homestead also includes agricultural land and facilities for domesticated animals. Where more secure dwellings are not available, people may live in the informal and sometimes illegal shacks found in slums and shanty towns. More generally, "home" may be considered to be a geographic area, such as a town, village, suburb, city, or country
News
News is the communication of selected[1] information on current events. It is shared in various ways: among individuals and small groups (such as by word of mouth or newsletters); with wider audiences (such as by publishing, either in print or online, or broadcasting, such as on television or radio); or in ways that blend those traits (such as when social media sharing starts among individuals but goes viral).
Code
<!-- replace 'top' with 'bottom', 'left' or 'right' to reposition navigation -->
<div class="ink-tabs top" data-prevent-url-change="true">
<!-- If you're using 'bottom' positioning, put this div AFTER the content. -->
<ul class="tabs-nav">
<li><a class="tabs-tab" href="#home">Home</a></li>
<li><a class="tabs-tab" href="#news">News</a></li>
</ul>
<!-- Now just place your content -->
<div id="home" class="tabs-content">
<h1 class="fw-300">Home</h1>
<p>
A home is a dwelling-place used as a permanent or semi-permanent residence for an individual, family, household or several families in a tribe. It is often a house, apartment, or other building, or alternatively a mobile home, houseboat, yurt or any other portable shelter. Larger groups may live in a nursing home, children's home, convent or any similar institution. A homestead also includes agricultural land and facilities for domesticated animals. Where more secure dwellings are not available, people may live in the informal and sometimes illegal shacks found in slums and shanty towns. More generally, "home" may be considered to be a geographic area, such as a town, village, suburb, city, or country
</p>
</div>
<div id="news" class="tabs-content">
<h1 class="fw-300">News</h1>
<p>
News is the communication of selected[1] information on current events. It is shared in various ways: among individuals and small groups (such as by word of mouth or newsletters); with wider audiences (such as by publishing, either in print or online, or broadcasting, such as on television or radio); or in ways that blend those traits (such as when social media sharing starts among individuals but goes viral).
</p>
</div>
</div>Tabs on the left
This example shows you how to change the position of the tabs to have them hanging from the left by adding the .left class to the .ink-tabs element. You can also use "top" (shown above), "bottom", or "right".
Demo
Home2
A home2 is a dwelling-place used as a permanent or semi-permanent residence for an individual, family, household or several families in a tribe. It is often a house, apartment, or other building, or alternatively a mobile home2, houseboat, yurt or any other portable shelter. Larger groups may live in a nursing home2, children's home2, convent or any similar institution. A home2stead also includes agricultural land and facilities for domesticated animals. Where more secure dwellings are not available, people may live in the informal and sometimes illegal shacks found in slums and shanty towns. More generally, "home2" may be considered to be a geographic area, such as a town, village, suburb, city, or country
News2
News is the communication of selected[1] information on current events. It is shared in various ways: among individuals and small groups (such as by word of mouth or news2letters); with wider audiences (such as by publishing, either in print or online, or broadcasting, such as on television or radio); or in ways that blend those traits (such as when social media sharing starts among individuals but goes viral).
Code
<div class="ink-tabs left" data-prevent-url-change="true">
<!-- If you're using 'bottom' positioning, put this div AFTER the content. -->
<ul class="tabs-nav">
<li><a class="tabs-tab" href="#home2">Home</a></li>
<li><a class="tabs-tab" href="#news2">News</a></li>
</ul>
<!-- Now just place your content -->
<div id="home2" class="tabs-content">
<h1 class="fw-300">Home2</h1>
<p>
A home2 is a dwelling-place used as a permanent or semi-permanent residence for an individual, family, household or several families in a tribe. It is often a house, apartment, or other building, or alternatively a mobile home2, houseboat, yurt or any other portable shelter. Larger groups may live in a nursing home2, children's home2, convent or any similar institution. A home2stead also includes agricultural land and facilities for domesticated animals. Where more secure dwellings are not available, people may live in the informal and sometimes illegal shacks found in slums and shanty towns. More generally, "home2" may be considered to be a geographic area, such as a town, village, suburb, city, or country
</p>
</div>
<div id="news2" class="tabs-content">
<h1 class="fw-300">News2</h1>
<p>
News is the communication of selected[1] information on current events. It is shared in various ways: among individuals and small groups (such as by word of mouth or news2letters); with wider audiences (such as by publishing, either in print or online, or broadcasting, such as on television or radio); or in ways that blend those traits (such as when social media sharing starts among individuals but goes viral).
</p>
</div>
</div>Style the active tab differently
The li containing the tab gets the .active class when it is active. You can use that as a CSS hook to style the active tab differently. .tabs-content also gets the .active class when it’s active.
Demo
Home2
A home3 is a dwelling-place used as a permanent or semi-permanent residence for an individual, family, household or several families in a tribe. It is often a house, apartment, or other building, or alternatively a mobile home3, houseboat, yurt or any other portable shelter. Larger groups may live in a nursing home3, children's home3, convent or any similar institution. A home3stead also includes agricultural land and facilities for domesticated animals. Where more secure dwellings are not available, people may live in the informal and sometimes illegal shacks found in slums and shanty towns. More generally, "home3" may be considered to be a geographic area, such as a town, village, suburb, city, or country
News2
News is the communication of selected[1] information on current events. It is shared in various ways: among individuals and small groups (such as by word of mouth or news2letters); with wider audiences (such as by publishing, either in print or online, or broadcasting, such as on television or radio); or in ways that blend those traits (such as when social media sharing starts among individuals but goes viral).
Code
<div class="ink-tabs top style-hook-example" data-prevent-url-change="true">
<!-- If you're using 'bottom' positioning, put this div AFTER the content. -->
<ul class="tabs-nav">
<li><a class="tabs-tab" href="#home3">Home</a></li>
<li><a class="tabs-tab" href="#news3">News</a></li>
</ul>
<!-- Now just place your content -->
<div id="home3" class="tabs-content">
<h1 class="fw-300">Home2</h1>
<p>
A home3 is a dwelling-place used as a permanent or semi-permanent residence for an individual, family, household or several families in a tribe. It is often a house, apartment, or other building, or alternatively a mobile home3, houseboat, yurt or any other portable shelter. Larger groups may live in a nursing home3, children's home3, convent or any similar institution. A home3stead also includes agricultural land and facilities for domesticated animals. Where more secure dwellings are not available, people may live in the informal and sometimes illegal shacks found in slums and shanty towns. More generally, "home3" may be considered to be a geographic area, such as a town, village, suburb, city, or country
</p>
</div>
<div id="news3" class="tabs-content">
<h1 class="fw-300">News2</h1>
<p>
News is the communication of selected[1] information on current events. It is shared in various ways: among individuals and small groups (such as by word of mouth or news2letters); with wider audiences (such as by publishing, either in print or online, or broadcasting, such as on television or radio); or in ways that blend those traits (such as when social media sharing starts among individuals but goes viral).
</p>
</div>
</div>
<style>
.style-hook-example .tabs-tab {
background: white !important;
transition: background-color 500ms ease;
}
.style-hook-example .active .tabs-tab {
background: #fdeca9 !important;
}
</style>Tabs options
data-prevent-url-change="true"- Don’t change the URL#hashwhen a tab is clicked.data-active="my-tab"- Activate the tab withid="my-tab"by default. Otherwise, it will be whatever is on the URL#hash, or the first tab in theul.data-menu-selector=".my-tabs-nav"- Your tab links. Use this if you don’t want to use the.tabs-navclass.data-content-selector=".my-tabs-content"- Your tab content panes. Use this if you don’t want to use the.tabs-contentclass.
Advanced Tabs stuff:
You can visit the Tabs API docs to find out about Javascript-only options, javascript methods, and how to create Tabs using Javascript
Toggle
Toggle is a component for showing and hiding things. It can be made to do far more.
Since “showing” and “hiding” is just adding and removing classes, by changing the added and removed classes, you can achieve a lot with styling hooks.
A Toggle can also coordinate with other sibling toggles and create an accordion using data-is-accordion="true".
Toggle examples
Simple Toggle
Demo
Code
<button class="ink-toggle ink-button" data-target="#myAlert">See more</button>
<div id="myAlert" class="ink-alert block hide-all">
<h4>This is a details section</h4>
<p>Insert awesome text here</p>
</div>Styling hooks for the toggle target
By using the data-class-name-on and data-class-name-off options you can customize what classes get added and removed from your toggle targets. Here’s how you choose between two classes on an element.
Demo
Code
<button class="ink-toggle ink-button" data-target="#myAlert2"
data-class-name-on="info"
data-class-name-off="error">Info or error?</button>
<div id="myAlert2" class="ink-alert block hide-all">
<h4>This is a details section</h4>
<p>Insert awesome text here</p>
</div>Styling hooks for the toggle itself
We can also style our button according to toggle state. Toggle will add the .active class to the toggle element, in this case the button.
Demo
Code
<button class="ink-toggle ink-button style-button-example" data-target="#myAlert3">Toggle something</button>
<div id="myAlert3" class="ink-alert block hide-all">
<h4>This is a details section</h4>
<p>Insert awesome text here</p>
</div>
<style>
.style-button-example.active {
background: #55c1bf !important;
}
</style>Multiple targets
Toggle is capable of toggling many targets. It will toggle everything you select in data-target.
Demo
Code
<button class="ink-toggle ink-button" data-target=".multitarget-example">Toggle something</button>
<div class="ink-alert block hide-all multitarget-example">
<h4>This is a details section</h4>
<p>Insert awesome text here</p>
</div>
<div class="ink-alert block hide-all multitarget-example">
<h4>This is a details section</h4>
<p>Insert awesome text here</p>
</div>
<div class="ink-alert block hide-all multitarget-example">
<h4>This is a details section</h4>
<p>Insert awesome text here</p>
</div>
<div class="ink-alert block hide-all multitarget-example">
<h4>This is a details section</h4>
<p>Insert awesome text here</p>
</div>Accordion
You can use Toggle to achieve an accordion! Just add the data-is-accordion="true" option to all accordion parts, and make sure they’re direct children of a div with the class .accordion.
Demo
See more 1
See more 2
See more 3
See more 4
Code
<div class="accordion">
<p>
<span class="ink-toggle ink-label yellow"
data-target="#accordion-1"
data-close-on-click="false"
data-is-accordion="true"
data-initial-state="true">See more 1</span>
</p>
<div id="accordion-1" class="ink-alert block hide-all" role="alert">
<p>Section 1</p>
</div>
<p>
<span class="ink-toggle ink-label yellow"
data-target="#accordion-2"
data-close-on-click="false"
data-is-accordion="true">See more 2</span>
</p>
<div id="accordion-2" class="ink-alert block hide-all" role="alert">
<p>Section 2</p>
</div>
<p>
<span class="ink-toggle ink-label yellow"
data-target="#accordion-3"
data-close-on-click="false"
data-is-accordion="true">See more 3</span>
</p>
<div id="accordion-3" class="ink-alert block hide-all" role="alert">
<p>Section 3</p>
</div>
<p>
<span class="ink-toggle ink-label yellow"
data-target="#accordion-4"
data-close-on-click="false"
data-is-accordion="true">See more 4</span>
</p>
<div id="accordion-4" class="ink-alert block hide-all" role="alert">
<p>Section 4</p>
</div>
</div>An Accordion inside an Accordion
Here’s how you put an accordion inside an accordion.
Just make sure to add the div with the class .accordion and place the inner accordion inside that. It should work well :)
Demo
See more 1
See more 2
See more 3
Code
<div class="accordion">
<p>
<span class="ink-toggle ink-label yellow"
data-target="#accordionception-1"
data-close-on-click="false"
data-is-accordion="true"
data-initial-state="true">See more 1</span>
</p>
<div id="accordionception-1" class="ink-alert block hide-all" role="alert">
<p>Section 1</p>
</div>
<p>
<span class="ink-toggle ink-label yellow"
data-target="#accordionception-2"
data-close-on-click="false"
data-is-accordion="true">See more 2</span>
</p>
<div id="accordionception-2" class="ink-alert block hide-all" role="alert">
<p>Section 2</p>
</div>
<p>
<span class="ink-toggle ink-label yellow"
data-target="#accordionception-3"
data-close-on-click="false"
data-is-accordion="true">See more 3</span>
</p>
<div id="accordionception-3" class="ink-alert block hide-all" role="alert">
<p>Section 3</p>
<div class="accordion">
<p>
<span class="ink-toggle ink-label yellow"
data-target="#accordionception-4"
data-close-on-click="false"
data-is-accordion="true">See more 4</span>
</p>
<div id="accordionception-4" class="ink-alert block hide-all" role="alert">
<p>Section 4</p>
</div>
<p>
<span class="ink-toggle ink-label yellow"
data-target="#accordionception-5"
data-close-on-click="false"
data-is-accordion="true">See more 5</span>
</p>
<div id="accordionception-5" class="ink-alert block hide-all" role="alert">
<p>Section 5</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>Toggle options
data-is-accordion="true"- This toggle is a part of an accordion. Make sure it is the direct child of an element with the class.accordion. Otherwise, Ink will warn you about this on the console.data-class-name-on="my-on-class"- Add the.my-on-classclass when the toggle is ON. Use this for styling hooks.data-class-name-off="my-off-class"- Add the.my-off-classclass when the toggle is OFF. Use this for styling hooks.data-close-on-click="false"- Don’t toggle OFF when clicking outside.data-can-toggle-an-ancestor="true"- Use this if you wish to toggle nodes which are ancestors of this node (for instance<div class="ancestor"><yourtoggleelement/></div>.data-close-on-inside-click=".some-class"- Toggle off when a child element with the class.some-classis clicked. By default toggle will toggle itself off when a link is clicked.data-initial-state="true"- Toggle is ON initially.data-initial-state="false"- Toggle is OFF initially.
Advanced Toggle stuff:
You can visit the Toggle API docs to find out about Javascript-only options, javascript methods, and how to create Toggles using Javascript
Tooltip
Tooltip examples
Simple Tooltip
Hover these labels:
Demo
Code
<span class="ink-tooltip ink-label green"
data-tip-text="Create a new document"
data-tip-color="green">
New
</span>
<span class="ink-tooltip ink-label red"
data-tip-text="Exit the program"
data-tip-color="red">
Quit
</span>
<span class="ink-tooltip ink-label blue"
data-tip-text="Save the document you are working on"
data-tip-color="blue">
Save
</span>Tooltip with arbitrary HTML inside.
You can set the tooltip’s inner HTML by using data-tip-html="(my html)".
Demo
Hover me
Code
<span class="ink-tooltip ink-label green"
data-tip-html="<h1>Random</h1><p>HTML</p><ul><li>content</li></ul>">
Hover me
</span>Change the default Tooltip template
You can replace the tooltip structure (the rounded rectangle with the triangle arrow) entirely by using data-tip-template="#my-template-id" and data-tip-templatefield=".write-tip-text-here".
Demo
Code
<span class="ink-tooltip ink-label blue"
data-tip-template="#tooltip-template"
data-tip-templatefield="span"
data-tip-text="Something I wish to write in that span">
hover me
</span>
<div id="tooltip-template" style="border: 1px solid gray; background-color: #eee; display: none">
<p><strong>A random tooltip template</strong></p>
<p><span>< tooltip text goes here :) ></span></p>
</div>Tooltip sides
Hover these labels:
Demo
Using data-tip-where="up" (default)
Using data-tip-where="down"
Using data-tip-where="left"
Using data-tip-where="right"
Using data-tip-where="mousemove"
Using data-tip-where="mousefix"
Code
<p class="ink-tooltip"
data-tip-where="up"
data-tip-text="up">
Using <code>data-tip-where="up"</code> (default)
</p>
<p class="ink-tooltip"
data-tip-where="down"
data-tip-text="down">
Using <code>data-tip-where="down"</code>
</p>
<p class="ink-tooltip"
data-tip-where="left"
data-tip-text="left">
Using <code>data-tip-where="left"</code>
</p>
<p class="ink-tooltip"
data-tip-where="right"
data-tip-text="right">
Using <code>data-tip-where="right"</code>
</p>
<p class="ink-tooltip"
data-tip-where="mousemove"
data-tip-text="mousemove">
Using <code>data-tip-where="mousemove"</code>
</p>
<p class="ink-tooltip"
data-tip-where="mousefix"
data-tip-text="mousefix">
Using <code>data-tip-where="mousefix"</code>
</p>Tooltip options
data-tip-text="<tooltip text!>"- Text content for the tooltip.data-tip-html="<tooltip inner HTML>"- HTML for the tooltip. Use this instead ofdata-tip-textwhen you need to add arbitrary HTML instead of just text.data-tip-where="down"- Make the tooltip appear below the element instead of above. You can also use'left'or'right'. See below to find out how to place the tooltip relative to the mouse.data-tip-color="red"- Make the tooltip be red! The tooltip can be coloredred,orange,blue,greenandblack. Default iswhite.data-tip-fade="0.5"- Take 0.5s to fade in and out.data-tip-forever="true"- Make the tooltip not disappear even if the mouse goes away. If FOREVER is too long to wait usedata-tip-timeoutto set a time to live.data-tip-timeout="10"- The tooltip will stay open for 10 seconds. Useful withdata-tip-forever="true", and it won’tdata-tip-delay="1.1"- Wait 1.1s before showing the tooltip. Useful to avoid getting the attention of the user unnecessarily.data-tip-template="#my-template"- An element to use as the tooltip template instead of the default rectangle and arrow. See above for an example.data-tip-templatefield=".write-text-here"- When usingdata-tip-template, tell Tooltip to write the text in the.write-text-hereelement.
Positioning the tooltip relative to the mouse
Positioning relative to the mouse is easy and requires only one of these options:
data-tip-where="mousemove"- Tooltip follows the mouse.data-tip-where="mousefix"- Tooltip stays in place where the mouse first touched the element.
When the tooltip is positioned relative to the mouse, these two allow you to tweak how far from the mouse they are.
data-tip-left="20"- place the tooltip 20px to the right of the mouse.data-tip-top="20"- place the tooltip 20px below the mouse.
Advanced Tooltip stuff:
You can visit the Tooltip API docs to find out about Javascript-only options, javascript methods, and how to create Tooltips using Javascript
TreeView
Shows elements in a tree view whose nodes can be expanded and contracted.
A TreeView consists of “nodes” and “children”, which are elements which have child nodes.
TreeView examples
Simple TreeView
Demo
Code
<ul class="ink-tree-view">
<li data-open="true">
<a href="#">root</a>
<ul>
<li><a href="#">child 1</a></li>
<li>
<a href="#">child 2</a>
<ul>
<li><a href="#">grandchild 2a</a></li>
<li>
<a href="#">grandchild 2b</a>
<ul>
<li><a href="#">grandgrandchild 1bA</a></li>
<li><a href="#">grandgrandchild 1bB</a></li>
</ul>
</li>
</ul>
</li>
<li><a href="#">child 3</a></li>
</ul>
</li>
</ul>TreeView options
data-node=".node"- Make tree nodes be elements with the.nodeclass instead of anylielement.data-children=".cont"- Make the children containers be elements with the.contclass.data-parent-class="i-am-parent"- Add the.i-am-parentclass to nodes which have children.data-open-class="fa fa-check-circle"- Add the.fa-check-circle,.faclasses to the icon when nodes are open. Use this to override the default icons.data-closed-class="fa-circle"- Add the.fa-circle,.faclasses to the icon when nodes are closed. Use this to override the default icons.data-hide-class="invisible"- Add the.invisibleclass to “children” elements to when they are hidden. Defaults tohide-all.data-icon-tag="span"- Use aspaninstead of anifor the icon.
Advanced TreeView stuff:
You can visit the TreeView API docs to find out about Javascript-only options, javascript methods, and how to create TreeViews using Javascript